
The main reason for scarfing is not to remove metal from the slab surface, but to remove the surface defects from the slab. From our experience, most of the defects are located within the first 1 to 2 mm of the surface, but frequently other defects can be found deeper in the slab.
When pouring ingots, cracks or impurities can quickly form and need to be removed. KATANA Cutting Systems provides a suitable solution with a variety of handheld torches and casting options available in different lengths and widths. Depending on the nozzle used, combinations of acetylene/oxygen or propane, methane, or coal gas with oxygen may be utilized. The Stellite wear ring ensures a long lifespan for the nozzle. Our complete range of accessories, such as thermal protection shields and hoses, makes your work easier and complements our selection of handheld or casting torches.
- Available lengths: 1300, 1500, 1600, and 1800 millimeters.
- Oxygen connection: G1/2″RH*
- Fuel gas connection: G3/8″LH*
- Equipped with an angled head 110˚.
- Scarfing width: 40~60 millimeters
- Features a spring lever for controlling oxygen during scarfing
- Gas combinations: propane, methane, coal gas, and oxygen (PM)
- Brass pressed body.
- Stainless steel oxygen and gas regulating taps.
- Stainless steel pipes.
- Aluminum heat protection shield.
In the design of KATANA model tips for scarfing torches, the structural details and installation method of the torch tip within the torch nozzle are precisely outlined.
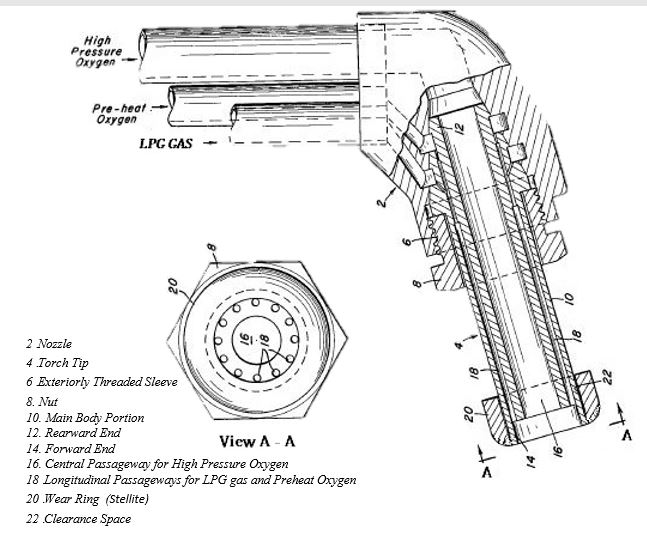
In this design, the torch tip (referenced as 4) is located within the nozzle (referenced as 2). The torch tip is constructed from a main body (referenced as 10) made of copper, which features a central passage (referenced as 16) for high-pressure oxygen flow and several longitudinal passages (referenced as 18) to direct acetylene and preheated oxygen to the front end.
New features of this design include a wear ring (referenced as 20) made of a wear-resistant material called Stellite, positioned near the front end of the body. This ring is designed with a clearance space (referenced as 22) to allow for expansion and contraction relative to the body.
Overall, this design focuses on utilizing the high thermal properties of copper and the specific flange design to enhance the efficiency and durability of the torch. These features contribute to improved torch performance and increased longevity in industrial processes.

